
- #Skippy algorithm disk graph full
- #Skippy algorithm disk graph registration
- #Skippy algorithm disk graph software
Parkinson’s Disease Pull Test Proxy Model Development using Daily Life Activities

Simulation study of Uncertainty Quantification on classification tasks using Empirical Bayesian Deep Neural NetworkĪdaptive Reinforcement Learning for Human-AI collaboration Topology-aware Network Feature Selection in Link PredictionĪspect-Based Sentiment Analysis on Dutch Patient Experience Survey Data
#Skippy algorithm disk graph software
Mining Physical Activity Behaviours in Older AdultsĪnalyzing the stress produced in Computer Science students during exams and the effects of gender stereotypesĮffects of symmetry breaking in the performance and the design of Quantum Approximate Optimisation Algorithm (QAOA).ĭata mining paper meta-data: a novel model for large scale paper meta-data researchįeature Extraction using Deep Learning for Breast Cancer Histopathology - CONFIDENTIALĪMOOSE: A Domain Specific Language for the Astrophysical Multipurpose Software Environment Network-driven analysis of evolving populations in genetic algorithms GreatAI: An easy-to-adopt framework for robust end-to-end AI deploymentsĬontent-agnostic cascade-wise ranking of Fake News on Online Social Media Style Matters: Evaluation on Communication Styles of a Restaurant RobotĪugmenting existing activity recognition classifiers for inactivity detection of the elderlyĬentrality-based NSGA-II method for optimal sensor placement in water distribution networksĪutomated drug repurposing workflow for rare diseasesĭeep Reinforcement Learning for Profiled Side-Channel Attacks Applying Proximal Policy Optimization for Point Of Interest Selection Multi-objective Optimization of Takeaway Order Allocation based on NSGA-II Algorithm
#Skippy algorithm disk graph registration
Meal Delivery Routing with Crowd-sourced VehiclesĮnginetron: realtime car exhaust note synthesis using on-board diagnostics through Text-to-Speech networksĪ Deeper Dive into the Relations Between Physical Activity and Cardiovascular Disease using Subgroup Set Discovery and a Smartphone-Based DatasetģD preoperative to intraoperative registration of lymph node locations in robotic prostate cancer surgeryĭetecting the switch time for informed one-shot dynamic algorithm selection using the area under the ECDF curve Predicting Treatment Response for a Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (MPM) Patient Based on the 3D Medical ImagingĮxploiting Temporal Context for Tiny Object Detection - CONFIDENTIALĪnalysing the inductive biases of equivariant quan- tum circuits For simplicity of discussion, we assume that every point of P lies in the interior of a cell of \(\varPsi _r(P)\). The first step is to implicitly build a grid \(\varPsi _r(P)\) of square cells whose side lengths are r/2. The WX algorithm can solve the problem in \(O(n\log ^2 n)\) time.įor any point p, denote by \(\bigodot _p\) the disk centered at p with radius r. Given P, r, and a source point \(s\in P\), we consider the SSSP problem to compute shortest paths from s to all points of P in the unit-disk graph \(G_r(P)\).

For any two points p and q in the plane, let \(\Vert p - q \Vert \) denote the Euclidean distance between them. As we will parameterize the WX algorithm, we first review the WX algorithm. We follow the notation introduced in Sect.
#Skippy algorithm disk graph full
Due to the space limit, many proofs and the discussion about the \(L_1\) problem are omitted but can be found in the full paper of (the two papers are merged). In the following, we tackle the \(L_2\) problem in Sects.
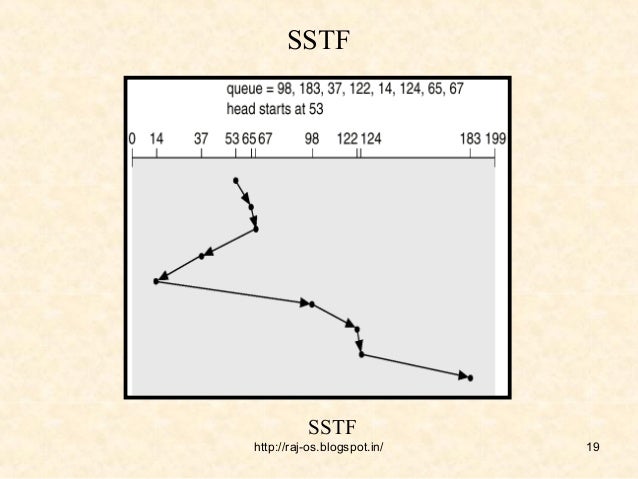
Given a set P of n points in the plane and a parameter r, the unit-disk graph \(G_\log ^2 n)\) time .


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
